U.S. central bank Fed adjusts to data-dependence (Martin Ertl)
- Mixed data signals magnify uncertainty about the state of the U. S. business cycle.
- On Wednesday, the Fed is unlikely to change its growth and inflation outlook significantly, however, it will be interesting seeing how its expectations about policy changes evolve.
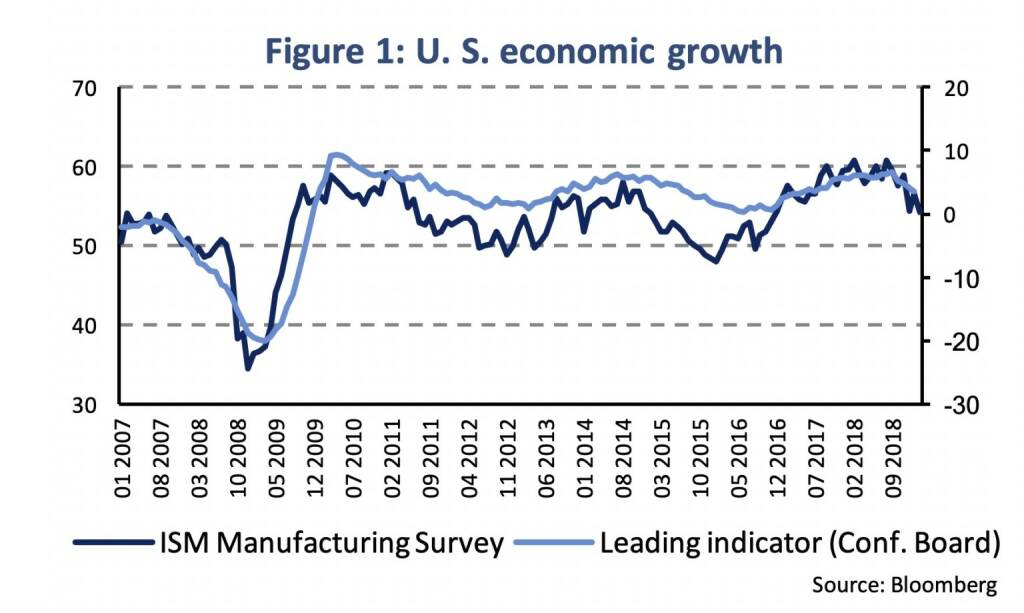
After a solid economic expansion until the end of last year (real gross domestic product increased by 2.4 % in Q4), the expectations for the current quarter growth have gradually diminished. Real-time GDP estimates from the Atlanta and New York Fed signal growth of meagre 0.4 % and 1.4 % (q/q, annualized rate) for Q1 2019. Other coincidence indicators (for example, the leading indicator of the Conference Board) or forward-looking surveys, like the ISM manufacturing survey, confirm slowing economic momentum (Figure 1). In January, growth in nation-wide industrial production slowed (3.8 % y/y), although retail sales rebounded (2.3 % y/y) after a sudden drop in December. The employment report revealed surprisingly weak job growth in February (20 thousand after 311 thousand new jobs in January). A gradual growth slowdown is widely expected. Moreover, uncertainty about the state of the U. S. business cycle has been heightening in the run-up of the monetary policy meeting (FOMC) on Wednesday 20th March.
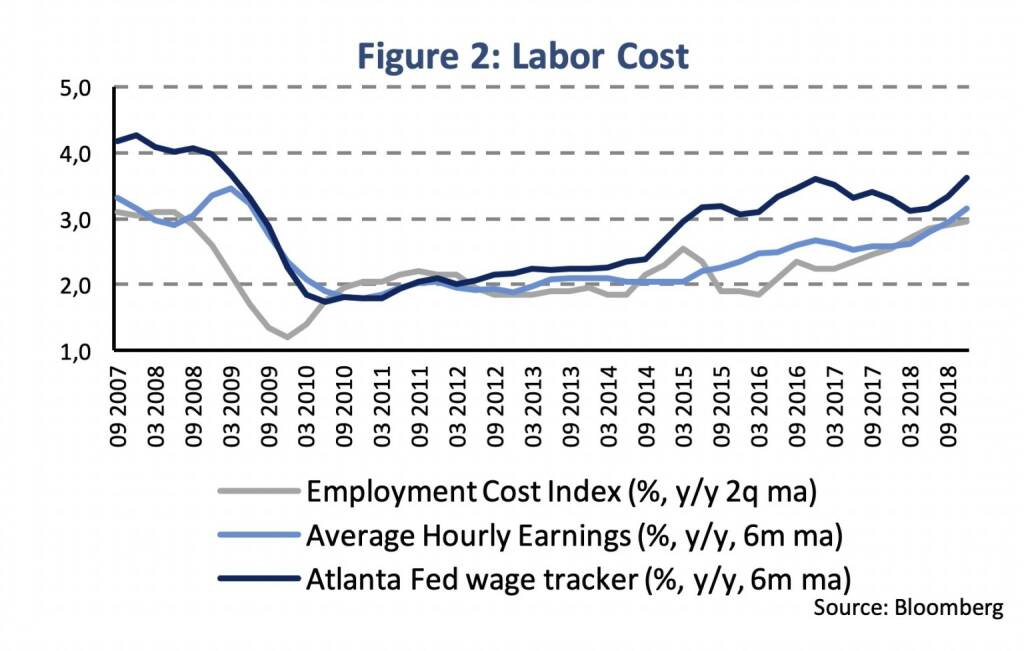
In February, the consumer price inflation rate (CPI) decreased to 1.5 % (following 1.6 % in January and 2.4 % on average during 2018). Average historical monthly CPI changes would suggest a pick-up of the inflation rate in March (~1.9 %), which would be in line with inflation forecasts for the entire year (f. ex. Bloomberg consensus: 1.9 %). The core inflation rate has been well anchored around the Fed’s 2 % inflation target (2.1 % in February). Several time series indicated gradually increasing wage pressure (Figure 2). In February, the average hourly earnings rose by 3.4 % compared to 3.0 % on average during 2018 indicating tight labor market conditions and fostering a sustained inflation trend.
The Fed stressed increasing risks to the economic outlook as well as muted inflation in the FOMC statement in January and shifted to a wait-and-see approach regarding further monetary policy changes. The FOMC patiently awaits greater clarity [1]. The quarterly summary of economic projections is going to be released on Wednesday. In December, the Fed had projected that real GDP will grow by 2.3 % and 2.0 % and that the personal consumption expenditure (PCE) inflation will be 1.9 % and 2.1 % in 2019/2020. These projections were roughly in line with current 2019 forecasts about U. S. growth and inflation (2.4 % and 1.9 % according to Bloomberg median forecasts). However, note that a pick-up in quarterly growth after a weak Q1 is built into these expectations.
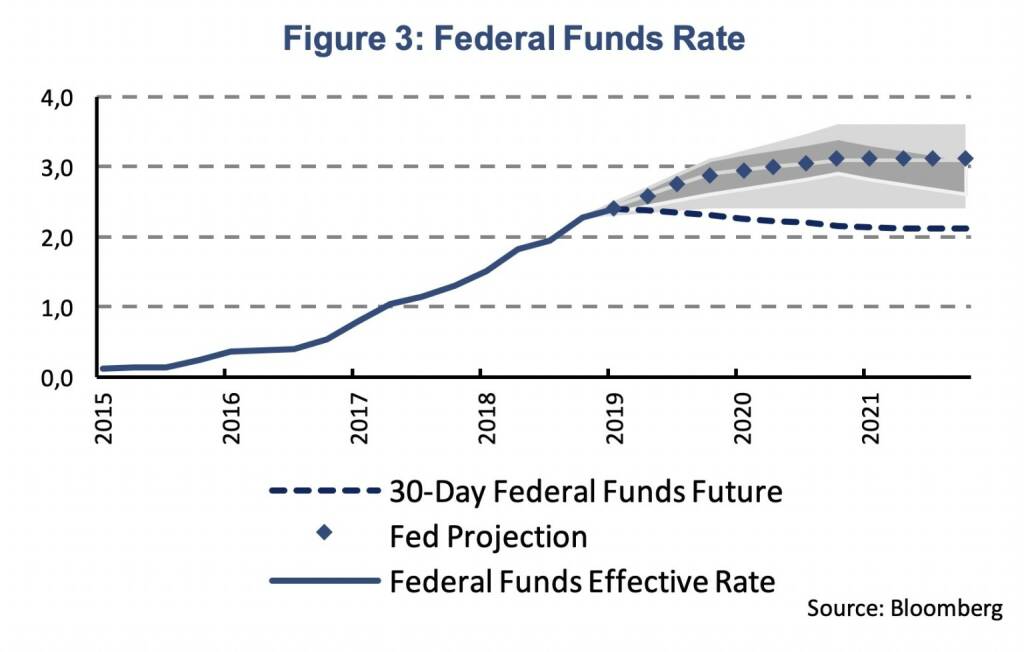
In the January statement, the FOMC made no more reference to further gradual increases in the federal funds rate emphasizing the data-dependency of future policy changes. Financial market participants have adjusted downwardly their expectations about the federal funds rate as indicated, for example, by federal funds rate futures (Figure 3).
In December, the median expectation among FOMC members was two fed funds rate increases in 2019 and one hike in 2020 (each 25 basis points). The federal funds rate is now within the broad range of estimates of the neutral rate – the interest rate that tends neither to stimulate nor to restrain the economy [2]. The inflation rate appears well anchored around the 2 % inflation target. The January FOMC statement made no indication of further gradual rate increases and the economic projections, which include expectations of FOMC members about the future rates path (“dots plot”), might adjust accordingly on Wednesday. On the other side, guidance about future cuts in the federal funds rate would likely warrant a further deterioration in the growth outlook. While uncertainty about the state of the business cycle increased, significant changes in growth and labor market forecast of the Fed seem unlikely at this stage.
[1] UNIQA Capital Markets Weekly as of 4thFebruary. http://press-uniqagroup.com/news-uniqa-capital-markets-weekly?id=79089&menueid=1686
[2] Remarks by Chair J. H. Powell at the 2019 SIEPR Economic Summit, Stanford Institute of Economic Policy Research, Stanford, California, March 8th, 2019
Authors
Martin Ertl Franz Xaver Zobl
Chief Economist Economist
UNIQA Capital Markets GmbH UNIQA Capital Markets GmbH
Latest Blogs
» SportWoche Podcast #124: Liam Ferguson, de...
» Österreich-Depots: Ultimo-Bilanz mit Addik...
» Börsegeschichte 30.8.: Warren Buffett (Bör...
» PIR-News: Zahlen von Warimpex, Strabag, Ne...
» Nachlese: Karin Bauer, LLB Aktien Österrei...
» Wiener Börse Party #727: Nächster Rekord-T...
» Börsenradio Live-Blick 30/8: DAX krönt Erh...
» Börse-Inputs auf Spotify zu u.a. ATX TR, L...
» ATX-Trends: Immofinanz, UBM, CA Immo, S Im...
» Börsepeople im Podcast S14/17: Karin Bauer
Weitere Blogs von Martin Ertl
» Stabilization at a moderate pace (Martin E...
Business and sentiment indicators have stabilized at low levels, a turning point has not yet b...
» USA: The ‘Mid-cycle’ adjustment in key int...
US: The ‘Mid-cycle’ interest rate adjustment is done. The Fed concludes its adj...
» Quarterly Macroeconomic Outlook: Lower gro...
Global economic prospects further weakened as trade disputes remain unsolved. Deceleration has...
» Macroeconomic effects of unconventional mo...
New monetary stimulus package lowers the deposit facility rate to -0.5 % and restarts QE at a ...
» New ECB QE and its effects on interest rat...
The ECB is expected to introduce new unconventional monetary policy measures. First, we cal...
