CEE and the global economy: The big picture (Martin Ertl)
- The global economic expansion is in full swing and accompanied by intensifying world trade.
- The growth outlook for the United States has brightened, also due to the tax reform, and the Euro Area is continuing its recovery.
- CEE remains Europe’s growth engine with GDP growth of 4.4 % in 2017 (y/y, excluding Russia).
- Monetary policy continues to be accommodative despite of a gradual normalization.
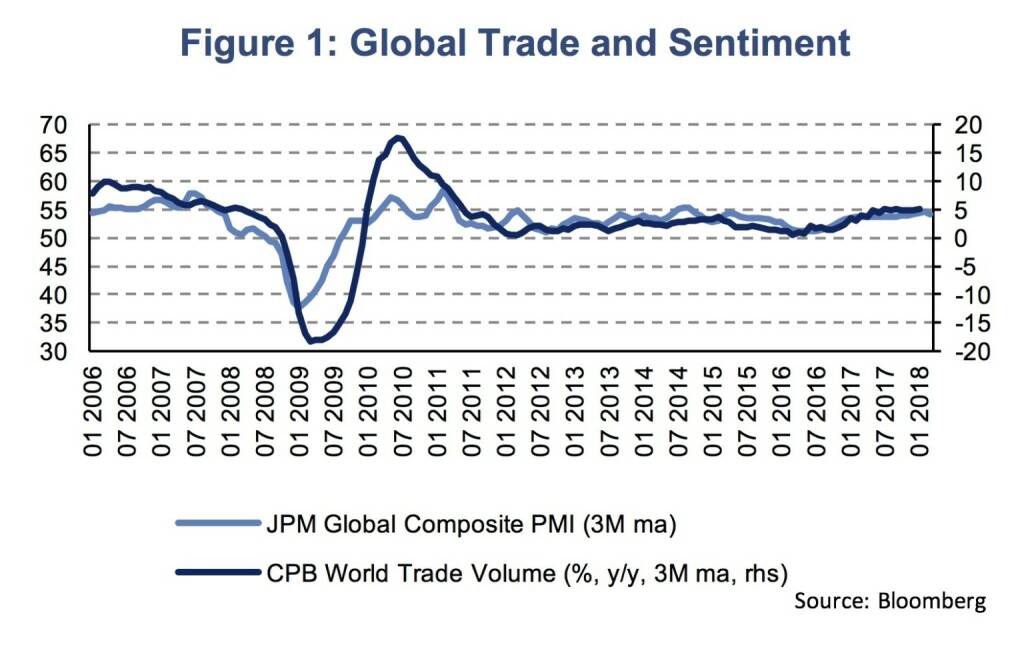
In 2017 we have seen the broadest synchronized global upsurge since 2010. The global economy expanded by 3.7 % (y/y) and according to the IMF’s latest update of its World Economic Outlook, global growth will be even higher, at 3.9 % (y/y), in 2018 and 2019. The prolonged growth momentum is supported by growing international trade. Growth in the volume of global trade has accelerated from 1.5 % in 2016 to 4.5 % in 2017. With the growing importance of international trade, uncertainties emerge from the protectionist shift of US trade policy. However, until now global sentiment indicators remain at elevated levels and global growth in the volume of trade has further accelerated to 5.6 % (y/y) in January 2018 (Figure 1).
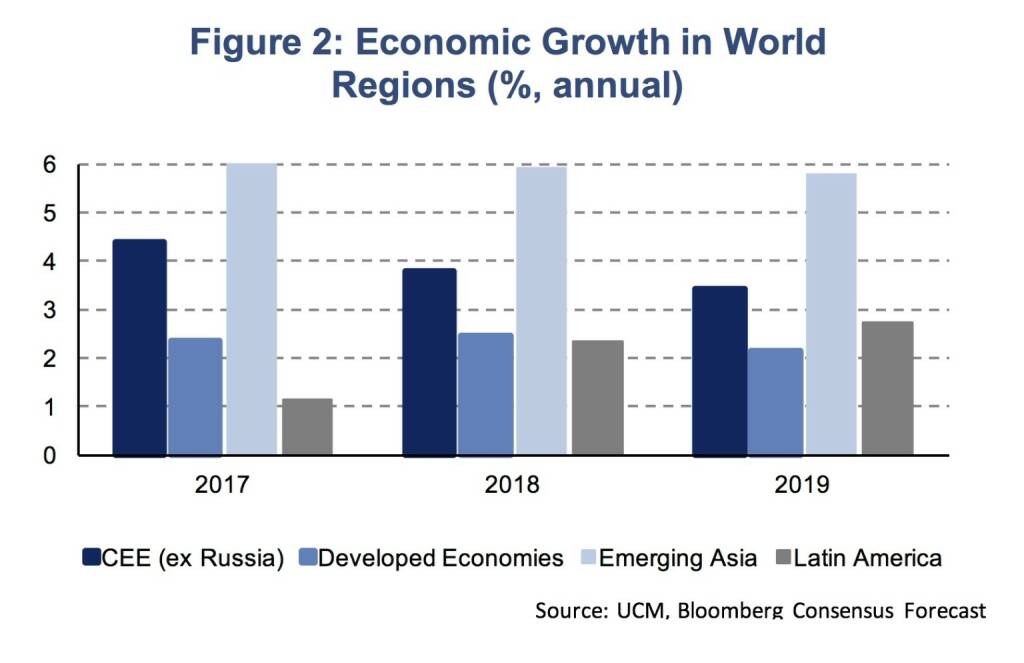
Both developed and emerging economies show continued growth momentum. The United States is the fastest growing advanced economic region with additional short-term stimulus from the US tax reform, even though its magnitude is subject to severe uncertainty and likely to be below 0.1 %-age points per annum over a 10-yer period. In the Euro Area, the recovery is continuing although a further business cycle acceleration has become more unlikely. Among emerging market economies, Emerging Asia and Emerging Europe are the fastest growing regions (Figure 2). The CEE region, in which UNIQA operates, was expanding at 4.4 % (y/y, excluding Russia) in 2017 and we expect growth to remain well above 3 % in 2018 (3.8 %) and 2019 (3.4 %).
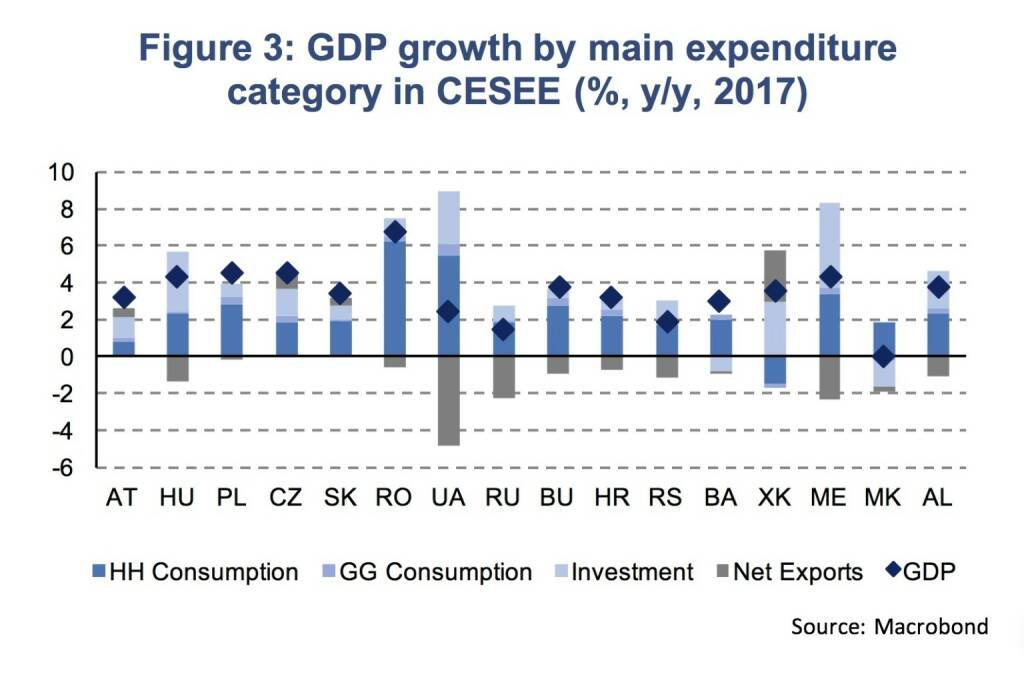
The CEE region remains Europe’s engine of economic growth. In 2017, domestic demand has been the primary growth driver (Figure 3). Decreasing unemployment rates and rising nominal and real wages have fuelled household consumption. Also, investment activity picked up markedly being supported by EU structural funds and accelerated construction activity. Net exports have only played a minor role, or contributed even negatively to GDP growth, as domestic demand fuelled import growth outpacing a decent export performance.
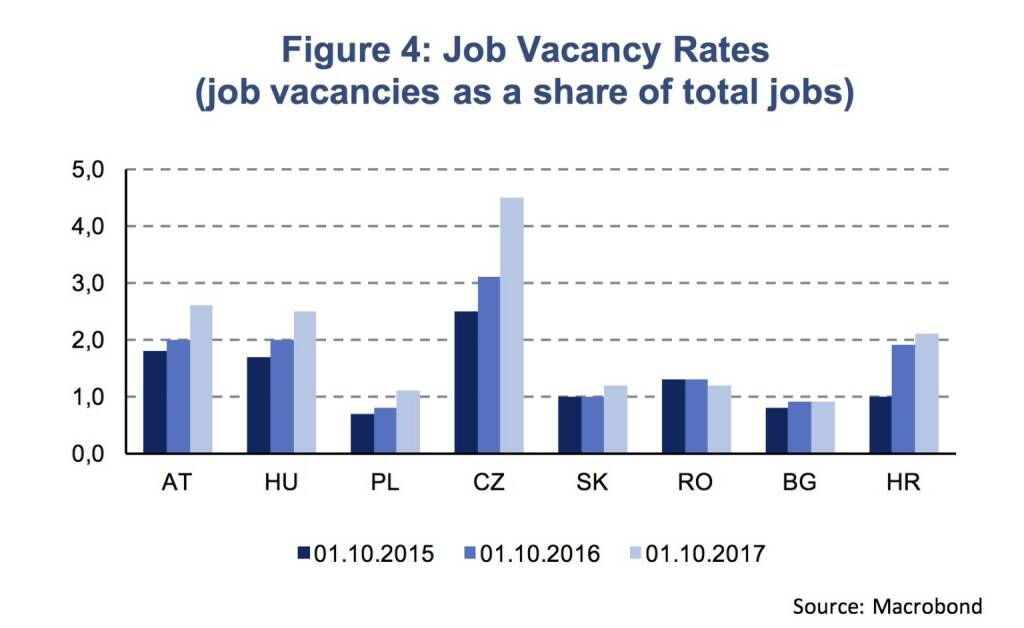
Among individual countries, Romania has achieved the highest growth rate in 2017 at 6.8 % (y/y). Growth rates above 4 % (y/y) were also achieved in Poland (4.6 %), the Czech Republic (4.5 %), Montenegro (4.4 %) and Hungary (4.2 %). At the same time, labor markets are becoming tighter and the unmet demand for labor rises. This is most pronounced in the Czech Republic as shown by job vacancy rates (Figure 4). Moreover, unemployment rates are at, or close to, their historic lows and have decreased considerably during the last years in most CEE economies. In Central Europe (Hungary, Poland, Czech Republic and Slovakia) the unemployment rate has come down to 4.7 % in 2017 from above 10 % in the 2010-2013 period. However, some economies of Southern Eastern Europe have structurally weak labor markets with elevated unemployment rates. Despite of significant decreases, still more than 20 % of the economically active population are without a job in countries like Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo or Macedonia.
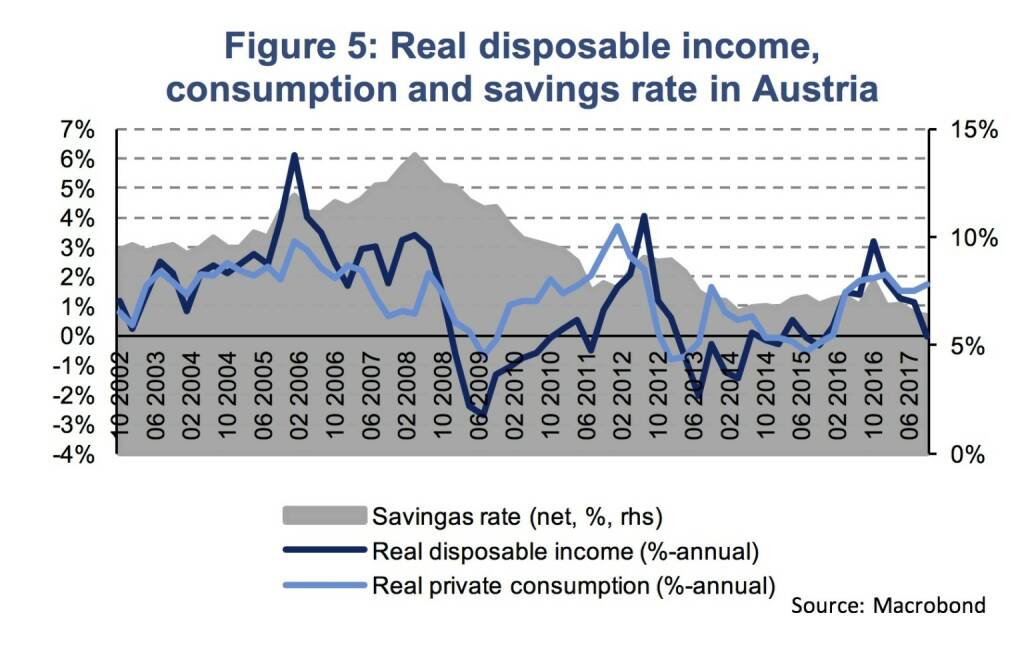
In Austria, the business environment remains very positive this year amid a strong GDP growth and the recovery in the labor market. In Q4, the Austrian real GDP rose 0.8 % quarterly and by 3.6 % in annual terms. Growth was well balanced in 2017, with household consumption, investment and net exports positively contributing to GDP growth. The rapid recovery of the labor market contributes to the positive sentiment among consumers. The unemployment rate has been decelerating (5.5 %, 2017, Eurostat, seasonally-adjusted). In 2017, real disposable income remained almost unchanged while private consumption expanded, hence, savings (as a percentage of income) declined to 6.4 % (a level below the pre-crisis average).
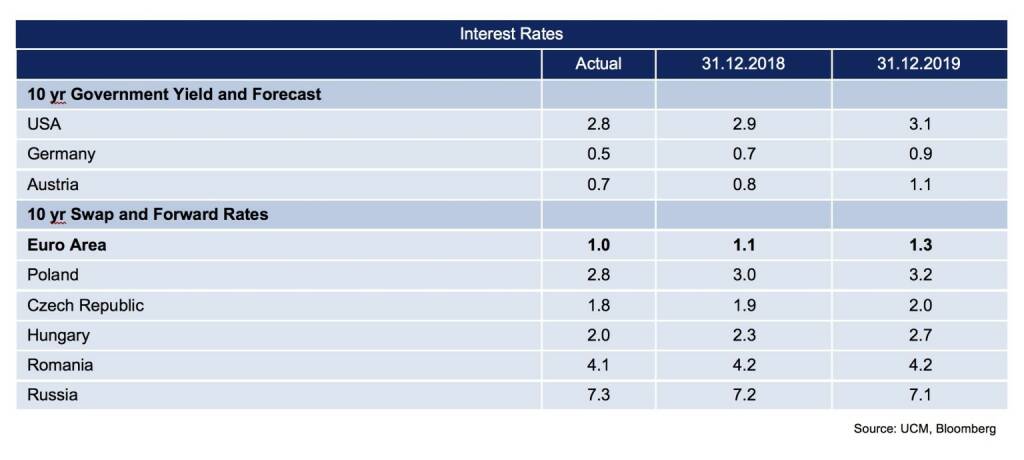
The global expansion is solid and balanced both among world regions and sectors. In this positive macro-economic environment, the US central bank Fed and the ECB pursue a gradual monetary policy normalization. Nevertheless, monetary policy continues to be accommodative. Expectations for higher interest rates have been building. The US Fed funds rate was raised to 1.75 % in March and the ECB is expected to start an interest rate hiking cycle in 2019. In the Euro Area, the inflation rate was low in February and is expected to rise gradually during the next months. The ECB’s net asset purchases (QE) of 30 bn EUR per month are intended to run until September and most likely will be gradually adjusted towards zero afterwards.
Authors
Martin Ertl Franz Zobl
Chief Economist Economist
UNIQA Capital Markets GmbH UNIQA Capital Markets GmbH
Latest Blogs
» BSN Spitout Wiener Börse: Wienerberger zur...
» SportWoche Party 2024 in the Making, 14. A...
» SportWoche Party 2024 in the Making, 15. A...
» Österreich-Depots unveändert (Depot Kommen...
» Börsegeschichte 18.4.: Mayr-Melnhof (Börse...
» SportWoche Party 2024 in the Making, 18. A...
» Reingehört bei A1 Telekom Austria (boersen...
» News von Verbund und VIG, Research zu Palf...
» Nachlese: Matejka Poetry Slam, B&C, 10% au...
» Wiener Börse Party #631: XXS-Folge mit ein...
Weitere Blogs von Martin Ertl
» Stabilization at a moderate pace (Martin E...
Business and sentiment indicators have stabilized at low levels, a turning point has not yet b...
» USA: The ‘Mid-cycle’ adjustment in key int...
US: The ‘Mid-cycle’ interest rate adjustment is done. The Fed concludes its adj...
» Quarterly Macroeconomic Outlook: Lower gro...
Global economic prospects further weakened as trade disputes remain unsolved. Deceleration has...
» Macroeconomic effects of unconventional mo...
New monetary stimulus package lowers the deposit facility rate to -0.5 % and restarts QE at a ...
» New ECB QE and its effects on interest rat...
The ECB is expected to introduce new unconventional monetary policy measures. First, we cal...
